How efficient is the lighting of LED bulbs? What are the criteria?
In the field of modern lighting, LED light bulbs have become one of the mainstream lighting solutions. Due to their unique energy-saving characteristics, long service life and environmental advantages, LED bulbs have been widely used around the world. With the continuous development of LED technology, consumers have higher and higher requirements for the lighting efficiency of LED light bulbs. However, many people still do not have a deep understanding of the concept of "lighting efficiency", especially in terms of how to measure the lighting efficiency of LED light bulbs. Therefore, this article will discuss in detail the two questions of "How efficient is the lighting of LED bulbs?" and "What are the criteria?" to help consumers and industry practitioners better understand this important performance indicator.

What is the lighting efficiency of LED bulbs?
Before understanding the lighting efficiency of LED light bulbs, we first need to clarify the concept of "lighting efficiency". Lighting efficiency usually refers to the luminous flux that a lamp can provide under unit power consumption, that is, the efficiency of the bulb converting electrical energy into light energy. Specifically, the higher the lighting efficiency of an LED bulb, the more light it can provide while consuming the same power.
The lighting efficiency of an LED bulb is an important indicator of LED lighting technology, which not only affects its performance, but also directly affects energy consumption and usage costs. Compared with traditional light sources such as incandescent lamps and fluorescent lamps, LED bulbs are widely regarded as an efficient lighting solution because they use solid-state light source technology, have higher light efficiency, lower power consumption and longer service life.
The lighting efficiency of LED bulbs is usually reflected in the following aspects:
● High light efficiency: LED light bulbs can output higher luminous flux with less electrical energy, thereby achieving higher lighting efficiency. Taking traditional incandescent lamps as an example, under the same energy consumption, LED light bulbs can provide more brightness and reduce energy waste.
● Low heat output: Compared with traditional light sources, LED light bulbs have higher light efficiency and less heat output. Traditional lamps convert a lot of energy into heat energy when emitting light, while LED bulbs convert almost all electrical energy into light energy, so their lighting efficiency is higher.
● Long life: The high efficiency of LED light bulbs not only means low energy consumption, but also means longer service life. The light source life of LED bulbs usually reaches tens of thousands of hours, which is also an important manifestation of its high lighting efficiency.
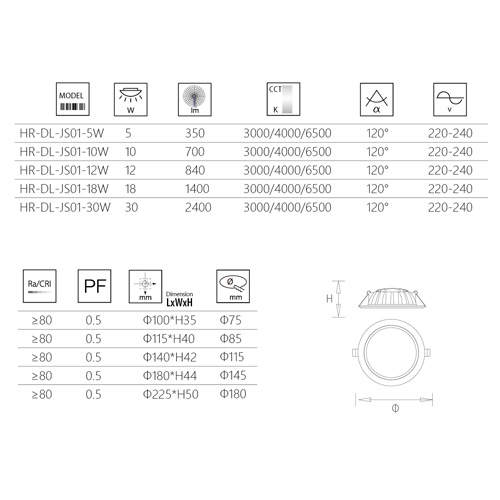
What is the measurement standard for LED bulb lighting efficiency?
The measurement standard for lighting efficiency is one of the core indicators for evaluating lamp performance. In the design and manufacturing process of LED bulbs, there are multiple standards and parameters used to measure and determine their lighting efficiency. The following are some common standards used to measure the lighting efficiency of LED light bulbs.
1. Luminous flux (Lumen, lm)
Luminous flux refers to the total amount of light emitted by a light source per unit time, and is the most commonly used standard for measuring lighting efficiency. Its unit is lumen (Lumen, lm). The greater the luminous flux, the more light output the LED bulb can provide per unit time, and the stronger the lighting effect. Generally, the luminous flux of an LED bulb is proportional to its power, that is, at the same power, the greater the luminous flux, the higher the lighting efficiency.
When measuring the lighting efficiency of an LED bulb, luminous flux is one of the most basic standards. When consumers buy LED bulbs, they usually pay attention to the lumen value of the bulb because it directly affects the brightness and lighting effect of the bulb. For example, the luminous flux of an LED bulb is generally marked as "1000 lumens" or "2000 lumens", which represents the total amount of light that the bulb can provide per unit time.
2. Power (Wattage, W)
Power is another important parameter for measuring lighting efficiency, and its unit is Watt (Watt, W). Power indicates the amount of electrical energy consumed by a lamp when it is working. A key point of lighting efficiency is to output more luminous flux with less power. For the same brightness lighting demand, the lower the power, the higher the energy efficiency of the LED bulb.
For example, traditional incandescent lamps generally have higher power. A 100-watt incandescent lamp can usually provide a luminous flux of 1,600 lumens, while a 14-watt LED bulb can also provide the same brightness, and its energy efficiency is much higher than that of traditional bulbs. This means that LED light bulbs consume much less electricity than incandescent lamps, which greatly reduces energy consumption and improves lighting efficiency.
3. Luminous Efficacy (lm/W)
Luminous efficiency is a more comprehensive indicator. It refers to the luminous flux generated by each watt of power consumption and is the core indicator for measuring the lighting efficiency of a light source. The unit of luminous efficiency is lumen per watt (lm/W). The higher the light efficiency, the more light the LED bulb can output at the same power, thus showing higher lighting efficiency in use.
The light efficiency of LED bulbs can usually reach 100 lumens/watt or even higher, while the light efficiency of traditional incandescent lamps is usually only 10-15 lumens/watt, and the light efficiency of fluorescent lamps is about 60-80 lumens/watt. Therefore, LED light bulbs can provide higher light output than traditional lamps at the same power, which means that it has higher energy efficiency and lower operating costs.
4. Color Temperature (Color Temperature, K)
Although color temperature is not directly related to lighting efficiency, it is also a factor that needs to be considered in lighting performance. Color temperature refers to the warmth or coolness of the light color of the light source, and the unit is Kelvin (K). Bulbs with lower color temperature have yellowish light, which is suitable for creating a warm and soft atmosphere; bulbs with higher color temperature have blue light, which is more suitable for working environments that require clear and bright.
The choice of color temperature is crucial to the lighting effect of LED bulbs. Although color temperature does not directly affect lighting efficiency, when choosing LED bulbs, a reasonable color temperature can ensure the best lighting effect and comfort. Different scenes have different lighting requirements, so the choice of color temperature should be combined with the actual environmental requirements.
5. Color Rendering Index (CRI)
The color rendering index (CRI) is a standard for evaluating the color rendering ability of a light source. The unit is a value between 0 and 100. The higher the value, the more natural the color of the object is. Although CRI itself does not directly affect the lighting efficiency of LED light bulbs, it is an indicator closely related to lighting quality. Generally, LED bulbs with a CRI value of more than 80 are considered to provide better color rendering and are suitable for home, commercial and professional workplaces.
A higher CRI value usually means a higher light quality, which can truly restore the color of objects and enhance the visual experience. Therefore, in certain specific lighting scenarios, such as art galleries, design studios, cosmetics stores, etc., consumers may pay special attention to the CRI value of LED bulbs.

How to calculate the lighting efficiency of LED light bulbs?
After understanding the measurement standard of lighting efficiency, we also need to explore how to calculate the lighting efficiency of LED bulbs. The lighting efficiency of LED bulbs is mainly measured by luminous efficacy (lm/W), which is calculated as follows:
1. Calculation formula for luminous efficacy
Luminous efficacy (lm/W) = Luminous flux (lm) ÷ Power (W)
For example, if the luminous flux of an LED bulb is 800 lumens and the power is 8 watts, its luminous efficacy is: Luminous efficacy = 800 lm ÷ 8 W = 100 lm/W
This means that the lighting efficiency of the LED bulb is 100 lumens per watt, indicating that its energy efficiency is quite high.
2. Factors affecting luminous efficacy
Factors affecting luminous efficacy include the light source efficiency of the LED bulb, the efficiency of the driving power supply, the design of the heat dissipation system, and the optical design of the lamp itself. For example, an efficient LED chip can output more light with less power, while an efficient power supply can reduce energy waste and further improve the luminous efficacy.
In addition, a good heat dissipation system can effectively reduce the operating temperature of the LED bulb, prevent excessive temperature from affecting the light source efficiency, and thus improve the luminous efficacy. Effective optical design can optimize the distribution of luminous flux and improve lighting effects through reasonable reflection, refraction and scattering.
